llama.cpp (Default)
Overview
Jan has a default C++ inference server (opens in a new tab) built on top of llama.cpp (opens in a new tab). This server provides an OpenAI-compatible API, queues, scaling, and additional features on top of the wide capabilities of llama.cpp.
llama.cpp Engine
This guide shows you how to initialize the llama.cpp to download and install the required dependencies to start chatting with a model using the llama.cpp engine.
Prerequisites
- Mac Intel:
- Make sure you're using an Intel-based Mac. For a complete list of supported Intel CPUs, please see here (opens in a new tab).
- For Mac Intel, it is recommended to utilize smaller models.
- Mac Sillicon:
- Make sure you're using a Mac Silicon. For a complete list of supported Apple Silicon CPUs, please see here (opens in a new tab).
- Using an adequate model size based on your hardware is recommended for Mac Silicon.
This can use Apple GPU with Metal by default for acceleration. Apple ANE is not supported yet.
- Windows:
- Ensure that you have Windows with x86_64 architecture.
- Linux:
- Ensure that you have Linux with x86_64 architecture.
GPU Acceleration Options
Enable the GPU acceleration option within the Jan application by following the Installation Setup guide.
Step-by-step Guide
Step 1: Open the model.json
- Navigate to the Advanced Settings.
- On the Jan Data Folder click the folder icon (📂) to access the data.
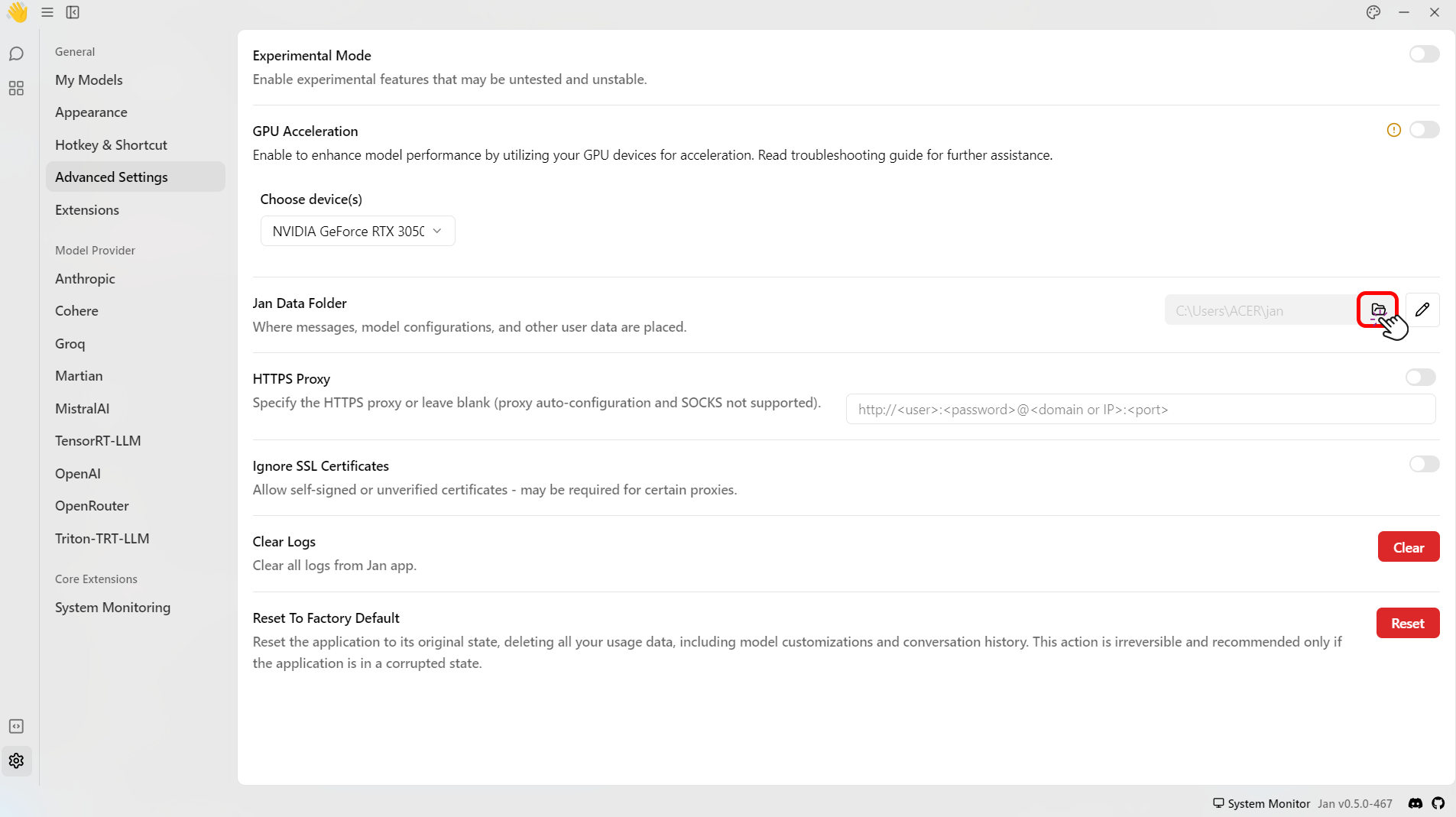
- Select models folder > Click the name of the model folder that you want to modify > click the
model.json. - This will open up a
model.json. For example, themodel.jsonofTinyLlama Chat 1.1B Q4is shown below:
{ "sources": [ { "filename": "tinyllama-1.1b-chat-v1.0.Q4_K_M.gguf", "url": "https://huggingface.co/TheBloke/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0-GGUF/resolve/main/tinyllama-1.1b-chat-v1.0.Q4_K_M.gguf" } ], "id": "tinyllama-1.1b", "object": "model", "name": "TinyLlama Chat 1.1B Q4", "version": "1.0", "description": "TinyLlama is a tiny model with only 1.1B. It's a good model for less powerful computers.", "format": "gguf", "settings": { "ctx_len": 4096, "prompt_template": "<|system|>\n{system_message}<|user|>\n{prompt}<|assistant|>", "llama_model_path": "tinyllama-1.1b-chat-v1.0.Q4_K_M.gguf" }, "parameters": { "temperature": 0.7, "top_p": 0.95, "stream": true, "max_tokens": 2048, "stop": [], "frequency_penalty": 0, "presence_penalty": 0 }, "metadata": { "author": "TinyLlama", "tags": [ "Tiny", "Foundation Model" ], "size": 669000000 }, "engine": "nitro"}
Step 2: Modify the model.json
- Modify the model's engine settings under the settings array. You can modify the settings with the following parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
ctx_len | Integer | Provides ample context for model operations like GPT-3.5. The default value is 2048 (Maximum: 4096, Minimum: 1). |
prompt_template | String | Defines the template used to format prompts |
model_path | String | Specifies the path to the model .GGUF file. |
ngl | Integer | Determines GPU layer usage. The default value is 100. |
cpu_threads | Integer | Determines CPU inference threads, limited by hardware and OS. (Maximum determined by system) |
cont_batching | Integer | Controls continuous batching, enhancing throughput for LLM inference. |
embedding | Integer | Enables embedding utilization for tasks like document-enhanced chat in RAG-based applications. |
- Save the
model.jsonfile.
If you use a different model, you must set it up again. As this only affects the selected model.
Step 3: Start the Model
- Restart the Jan application to apply your settings.
- Navigate to the Threads.
- Chat with your model.
- To utilize the embedding feature, include the JSON parameter
"embedding": true. It will enable Nitro to process inferences with embedding capabilities. Please refer to the Embedding in the Nitro documentation (opens in a new tab) for a more detailed explanation. - To utilize the continuous batching feature for boosting throughput and minimizing latency in large language model (LLM) inference, include
cont_batching: true. For details, please refer to the Continuous Batching in the Nitro documentation (opens in a new tab).
If you have questions, please join our Discord community (opens in a new tab) for support, updates, and discussions.